Jaundice In Children – Symptoms And Treatment

Jaundice in babies is a condition that is identified by yellowing of the skin and sclera of a newborn’s eyes. While it is usually not a serious condition, it needs to be evaluated by a physician.
Jaundice in babies is a condition characterized by changes in the color of the newborn’s skin and scleroderma (whites of the eyes) which turn yellowish. It develops due to an excessive build-up of bilirubin in the blood.
Bilirubin is a yellow pigment formed by the normal breakdown of red blood cells. This substance usually passes through the liver and is then released into the intestine as bile.
Although it is not a disease in itself, it should be taken as a warning sign as it may indicate an undiagnosed disease. However, in most cases it is temporary and harmless and responds well to non-invasive treatments. Still, you should always see a doctor to rule out any pathology.
Why do babies develop jaundice? How to identify her? As parents, we should be able to answer these questions. Therefore, we want to look at the causes, symptoms and treatments that will help control this disease.
Jaundice – causes
It is normal for infants to have a slightly higher bilirubin level at birth. In fact, most newborns have a yellowish skin color (jaundice). The condition develops in 80% of premature babies and 60% of full-term babies.
However, it is not always felt and may disappear on its own after about two weeks. Its main cause is the immaturity of the baby’s liver, which is unable to properly process bilirubin. Apparently, newborns produce more bilirubin because they renew red blood cells more often.
Other possible causes include:
- Family history of jaundice
- Not taking breast milk
- Internal bleeding
- Infection in the baby’s blood (sepsis)
- Viral or bacterial infections
- Incompatibility between the mother’s blood and the baby’s blood
- Liver failure
- Abnormalities in the red blood cells of the newborn
- Bile duct atresia
Symptoms of jaundice
In addition, when it occurs, it may be accompanied by:
- Incorrect nutrition
- Body weight below normal
- Sharp cry
- Tired look
Diagnosis
The doctor may diagnose jaundice in babies depending on the appearance of the newborn. However, other follow-up tests are required to measure blood bilirubin levels. In addition to the physical examination, the following tests are suggested:
- Laboratory test of your baby’s blood sample (complete blood count or blood count).
- Analysis with a device called a “percutaneous bilirubinometer”.
- test Coombs
- The number of reticulocytes

Treatment of jaundice in children
Infant jaundice usually resolves on its own within two or three weeks without treatment. However, when it arrives in moderate to severe condition, it is likely that the newborn baby has to stay in the hospital for several days.
Control measures will depend on the level of bilirubin in the blood, the age of the baby, and whether it was born prematurely. Your baby will need treatment if the bilirubin is very high or growing very quickly. The therapy includes:
Phototherapy
The child is exposed to a special lamp that emits light in a blue-green shade. This light is designed to break down the bilirubin molecules so that it can be excreted in the urine or faeces. It is not ultraviolet light and has a plastic cover that acts as a filter.
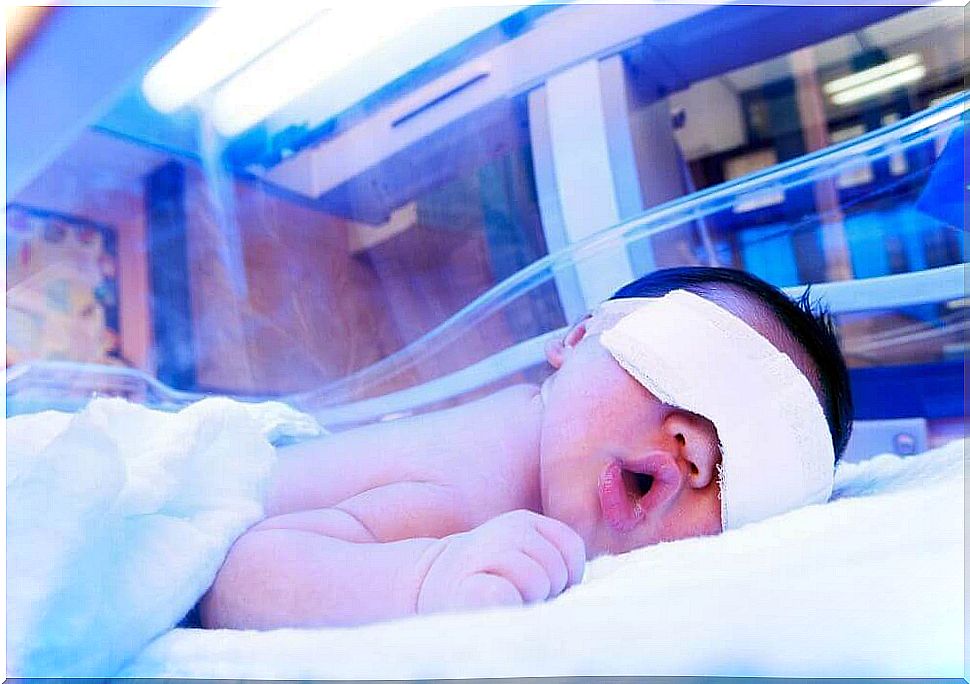
In addition, your baby will only wear diapers and protective blindfolds during treatment. In some cases, a light-emitting pillow or mattress may be used.
Intravenous Immunoglobin (IVIG)
Blood transfusion
In the few cases where there is no positive response to other therapies, infant jaundice requires a transfusion. It involves drawing small amounts of blood repeatedly to dilute the bilirubin and antibodies from the mother. The blood is then donated back to the baby.
Eating habits
If your baby’s jaundice is not severe, your doctor will recommend simple changes to your eating habits. Some mums need support because they have problems with breastfeeding. The following tips can help reduce jaundice:
- Breastfeed more often to help your baby defecate more often.
- By using complementary feeding, such as formula milk, when there are problems with breastfeeding. It is imperative to use this measure, especially when the newborn is losing weight or is dehydrated.
- Use artificial milk for a few days and then resume breastfeeding (only after consulting your doctor).

When to see a doctor
All babies should be evaluated by a specialist during the first five days of life to determine if they have jaundice. It is important to go to the hospital if yellowing is accompanied by fever, lack of appetite or apathy.
Jaundice is not dangerous in babies who are full-term or who have no other medical conditions. Therefore, if it is a premature baby it requires special attention. Some complications include acute bilirubin encephalopathy, cerebral palsy, and deafness.