Lung Cancer – Symptoms And Treatment Methods

Lung cancer is an insidious disease that initially gives no obvious symptoms. Only later – and often by accident – can cancer cells be detected in the lungs, as well as in other organs and tissues of the body.
The body’s cells divide and when they are destroyed, they quickly produce new ones. When this process gets out of hand, too many new cells are formed, and that’s how tumors form.
The lungs are a key organ of the respiratory system. Air through the nose and mouth goes to the trachea, from which it goes to the bronchi and finally – to the lungs. The lungs fill with air, thanks to which the body receives the right dose of oxygen. On the other hand, when you exhale, your body releases carbon dioxide.
That is why, since the lungs are responsible for the most vital functions of life, lung cancer – especially malignant – poses a huge threat not only to your health, but also to your life. It is one of the most common causes of death among cancer diseases.
Lung cancer – types
Lung cancer can be divided into different subtypes depending on the type of malignant cells seen under the microscope. The most common type of cancer is non-small cell carcinoma (NSCLC), but even this type is not completely uniform:
- Squamous cell carcinoma (SCC): As the name suggests, this type of cancer is characterized by the flattened shape of the malignant cells, somewhat elliptical or fish-like.
- Large cell carcinoma (LCC): A cancer that results from the presence of many different types of large malignant cells.
- Adenocarcinoma (AC): A type of cancer where cancer cells are found in the lining of the air sacs of the lungs to produce a type of discharge.
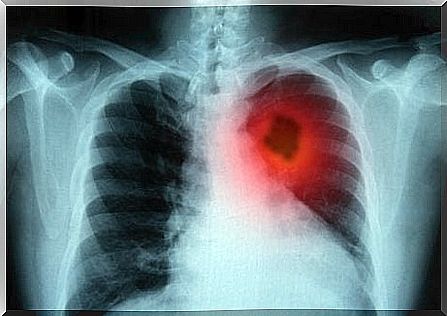
Less common subtypes also include neoplasms such as pleomorphic (polymorphic) tumors, salivary gland carcinoma, and other unclassified types of tumors and malignant cells.
Risk factors
Of course, the risk of developing any type of cancer can never be completely ruled out, but there are certain factors that greatly increase this chance.
- People addicted to nicotine are up to 90% more likely to develop lung cancer than non-smokers.
- The risk of developing the disease is also greater among people exposed to so-called ‘second-hand smoke’ and heavy environmental pollution.
- Additionally, any contact with substances such as arsenic, silicon and chromium increases the risk of getting sick.
How is lung cancer diagnosed?
It is not possible to completely and systematically define the clinical profile of a patient suffering from lung cancer. The symptoms and types of cells differ depending on the individual characteristics of each person, as well as the factors that led to the development of the disease.

However, there are a few characteristic symptoms that may be cause for concern and should definitely make you see a doctor:
- chronic and worsening cough
- pain in the chest
- breathing problems
- coughing up blood and rusty phlegm
- hoarse voice
- unreasonable weight loss
- recurring infections, pneumonia or bronchitis
- wheezing in the chest
When cancer cells appear in other organs and parts of the body, symptoms such as:
- yellowing of the skin (if metastases appear in the liver)
- bone pain
- headaches
- weakness in the arms and legs
- dizziness
- seizures
- enlarged lymph nodes
If these symptoms persist for at least three weeks, it is worth visiting a doctor who will probably start the diagnosis by ordering a chest X-ray. X-rays together with a detailed history of the disease will allow you to diagnose whether there is a lung cancer behind your ailments.
Diagnostic tests
Sometimes it is possible to detect neoplastic disease before the first symptoms described above appear. It happens most often due to preventive examinations, such as:
- Medical history : Your doctor checks your general health, examines your lymph nodes and auscultates your chest. He also inquires in detail about family history and health, as well as medications and habits.
- Laboratory tests: Signs of cancerous cells can be detected in blood, urine and tissue samples.
- Genetic tests: Genetic tests are most often aimed at people whose family has had cases of cancer, although other people interested in their health may also benefit from them.
- X- rays : X- rays can examine entire areas of the body where cancerous cells may be present.
Attention! Remember never to diagnose or self-medicate. Go to a specialist and use all tests and therapies under his supervision and strict control. Only thanks to this, the diagnosis will be accurate and the treatment possible and safe.
Methods of treating lung cancer
Lung cancer can be treated differently depending on the spread of the malignant cells in the body and the severity of symptoms.
Most often it is one of the following types:
- Surgical treatment: Cancer cells are surgically removed.
- Chemotherapy: Special drugs are used in the form of tablets or drips, the active substances of which are to destroy diseased cells.
- Radiation therapy: Cancer cells are hit by strong radiation.
- Targeted therapy: A special type of drug is intended to strike directly at the way and process of forming cancer cells.
Prevention of neoplastic diseases
In the case of neoplastic diseases, not only lung cancer, there are at least several rules of general prevention. Some of them are:
- Quit smoking and avoid being in smoky rooms.
- Increase the consumption of vegetables and fruits.
- Exercise regularly.
- Avoid burning in the fireplace and staying outside when air pollution is extremely high.
- Limit your alcohol consumption.
- Regularly perform preventive examinations that will reveal any irregularities.