Teeth Problems In Children – Learn About The Most Important Of Them

Teeth problems in children can affect oral functions such as speaking, chewing and eating. It can also affect the appearance of a smile, causing young children to have self-esteem difficulties and insecurity.
For this reason, oral care from an early age is of fundamental importance. And it is the parents’ responsibility. Therefore, they should pay special attention to the proper development of teeth and jaw, to possible injuries of the mucosa and cavities in the teeth.
Helping children to adopt healthy habits from an early age is also the responsibility of adults. It is better to prevent dental problems than to solve them later with more strenuous treatments.
In this article, we will tell you what are the most common dental problems in children. We will also explain their causes, how to solve them and what can be done to avoid them.
What can cause dental problems in children?
There are many changes that can occur in the mouth of young children, and each of them has specific causes. In any case, there are a number of factors that often affect:
- Heredity : The shape and size of the jawbones and teeth are determined by genetic factors. In some cases, they predispose to certain pathologies of the oral cavity.
- Bacterial plaque: a layer formed by food debris and microorganisms that adheres to the surfaces of the teeth and mucous membranes. Its accumulation as well as acids produced by bacteria favor the development of the most common diseases.
- Diet: Many dental pathologies depend on the type and quality of food consumed. High consumption of sugar-rich foods promotes the growth of bacteria. On the other hand, malnutrition and calcium-poor diets may also be responsible for various dental problems in children.
- Dysfunctional habits: Repetitive habits that occur in a child and extend over time can affect oral health. Nail biting, mouth breathing, thumb sucking, using a pacifier or bottle, or sticking your tongue between your teeth when swallowing are just some examples of these harmful habits.
Cavities are the main dental problems in children
Caries is one of the most common dental problems in children. This disease occurs as a result of the demineralisation of the teeth due to the action of acids produced by bacteria in the mouth.
Microorganisms in the plaque ferment dietary sugars and produce acid that removes minerals from the tooth’s tissues. The main causes of this disease are related to high consumption of sweet foods and poor oral hygiene.
At the beginning of the disease, dry white spots can be seen on the surface of the teeth. As the lesions progress, they turn brown or black and the dental tissue breaks down, causing cavities and fissures.
Tooth decay in infants or early childhood caries is a form of disease that affects young children. These are changes that progress quickly and mainly affect the front teeth. They are caused by frequent consumption of sweet drinks that stick to the surface of the teeth and poor oral hygiene.
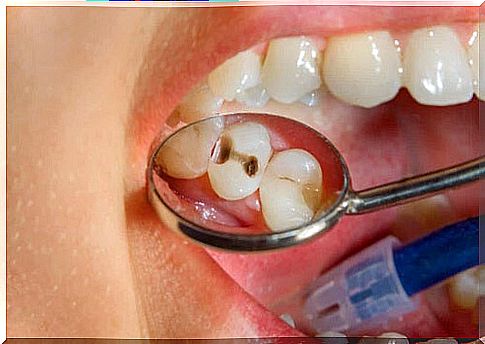
Complications of caries
If this disease progresses and is not treated, it can cause the following complications in young children:
- Pain: If the lesions get worse, they extend to the area of the dental pulp, where the nerve endings are. This causes increased sensitivity and pain in the affected tooth.
- Destruction: As the disease progresses, tooth tissue is lost and the affected parts crumble and disintegrate. Broken teeth can lead to malocclusion and bite problems.
- Infections: the bacteria responsible for decay can cause infections in the tooth or in the surrounding tissues.
- Permanent tooth damage: If decay affects a deciduous tooth and progresses without treatment, it can affect the correct formation of a permanent tooth that forms underneath.
Treatment of caries in children
The choice of therapy depends on the size of the lesion, the tissues involved and the development time of the process. If caries is detected early, the use of fluoride and changing hygiene habits may be enough to reverse the disease process.
Once there is a loss of tissue, it is necessary to clean the tooth and rebuild it with fillings that restore the shape of the tooth. Caries should always be treated and its development slowed down, as this will avoid later complications.
Teeth problems in children also apply to gingivitis
Although this disease is not as common in children as it is in adults, it is nevertheless closely related to poor oral hygiene. It is an inflammation of the gums caused by irritation due to the accumulation of bacterial plaque on them.
Gum tissue swells, turns dark red and bleeds easily. It can also be painful and disturbing, and your baby has bad breath.
Controlling plaque with good hygiene habits, such as proper brushing and flossing, is usually sufficient to treat the condition. In any case, it is advisable to consult a dentist for specific indications.
Malocclusion
Malocclusion is a common dental problem in children. The way the upper jaw fits over the lower jaw is disturbed or the position of the teeth in the arch is incorrect.
These problems disrupt oral functions such as biting, speaking and swallowing. In addition, they affect the appearance of the smile and the overall face of the patient.
It is necessary to detect them as soon as possible, because early treatment brings better results. In addition, it lasts shorter and causes less discomfort for the patient. Therefore, adults should pay attention to the way the child bites and the position of the teeth during eruption.
Frequent visits to the dentist also allow for early diagnosis of any bite irregularities.
There are several factors that can cause this type of bite disorder:
- Genetic factors: sizes of teeth or jaws that repeat in several family members.
- Dysfunctional habits: finger-sucking, prolonged use of a bottle or nipple, mouth breathing, or unusual swallowing are just some examples of repetitive habits that can change the way babies bite.
- Premature loss of deciduous teeth: If the deciduous teeth drop out prematurely due to cavities, infections, or trauma, they do not serve as a site preparation for permanent teeth. As a consequence, the latter erupts in the wrong places, disturbing the bite.
Treatment of malocclusion in children
Orthodontic treatment is essential to solve these types of dental problems in children. The choice of the type of appliance depends on the type of malocclusion, the patient’s age and the severity of the case.
Interoceptive orthodontics can provide benefits when the patient still has milk teeth in the mouth and bone growth needs to be monitored. When the eruption of fixed elements ends, fixed appliances are usually used, with different options depending on the needs.
Today, the use of Invisalign clear aligners also provides a good alternative for treating these problems in children and adolescents.
Teeth problems in children resulting from trauma
Oral injuries cause dental problems in children that occur regularly. The causes of these blows to the teeth are accidents that occur in the home environment, for example when the child is learning to walk, while playing or playing sports.
Injury can damage both deciduous and permanent teeth. The upper incisors are the most likely victims due to their most exposed position.
Tooth injuries can damage part of the tooth crown and even break the tooth completely, move it out of place or throw it out of the mouth. They are usually accompanied by pain, soft tissue bleeding, and a lot of stress and nervousness about the situation.
Treatment will depend on the tissues affected and the type of dentition. But in the event of a blow to the mouth, immediate consultation with a dentist is recommended. If the tooth is completely removed, find it and transport it in a saline solution or milk.
As already mentioned, the dentist decides which treatment is best. In a specific clinical case, it may recommend, among others:
- Fluoride placement and subsequent checks.
- Supplement or filling.
- Root canal treatment.
- Reimplantation of the tooth element and immobilization with splints.
Immediate dental consultation as soon as an accident occurs improves the prognosis of these dental problems in children. A diet with soft ingredients and careful oral hygiene as well as regular check-ups will also help.
When should you go to the dentist?
Parents often ask themselves when they should take their children to the dentist. Some people believe that you should only consult if you develop symptoms in your mouth.
The truth is, children should see the dentist for the first time before their first birthday, even if there is no apparent problem in the mouth. During the consultation, the dentist will examine the child’s mouth to detect any problems. In addition, parents are given advice on oral care.
Early detection of dental problems allows you to avoid complicated, inconvenient and even very often more expensive procedures. Moreover, complications related to the advancement of the disease can be prevented and pain situations in children can be avoided.
Checks are therefore necessary every six months to follow the evolution of jaw growth and the eruption of teeth. In addition, a doctor can diagnose any condition that arose during this time. In some cases, a specialist may suggest more frequent check-ups if justified by a higher risk of certain pathologies.
Recommendations and prevention of oral problems
The many dental problems we mentioned are common but preventable. Oral hygiene habits from an early age and the practice of healthy behaviors are essential.
Following these tips can help prevent many dental problems in children:
- Take care of proper oral hygiene: cleaning your mouth should be started as soon as possible, before the teeth are erupting. In young children it is done with moist gauze. This should be done by adults until the child is able to do it properly on their own. Teeth, gums and tongue should be washed three times a day with a soft brush and fluoride toothpaste. Cleaning is completed with floss and, if the dentist recommends it, with tooth rinses for children.
- Follow a healthy diet: maintaining a varied diet, rich in nutrients and with an adequate supply of calcium and vitamins, promotes the proper development and growth of children. Foods rich in refined sugars, such as sweets, cookies, and refreshing drinks should be avoided. Don’t give your baby sweet drinks or dip the teats in honey or sugar to soothe your baby.
- Control and eliminate dysfunctional habits: Eliminate repetitive and harmful oral practices such as finger sucking and using a bottle or nipple after the age of 2. Problems such as onychophagy (nail biting), unusual swallowing, or mouth breathing should also be dealt with.
- Put on your child’s mouth guards: Wearing these accessories while playing sports can help prevent tooth injuries.
- Don’t forget to visit the dentist: Early and regular visits to the dentist allow for early detection and treatment of any problems. In addition, the dentist is the best way to help adults take care of their children’s mouths. In-office preventive practices, such as sealing pits and fissures or using fluoride, help prevent dental problems in children.
Avoid dental problems in children
Various dental problems in children can occur as early as infancy. They disrupt not only the functions of the oral cavity (eating, talking and chewing). Later in life, they can also hinder relationships, generating problems with self-confidence and self-esteem.
Therefore, early and regular visits to the dentist are essential in this context, as are healthy oral practices and hygiene. Healthy lips ensure a happy smile from childhood to adulthood.